使用 window.performance 提供了一组精确的数据,经过简单的计算就能得出一些网页性能数据。
配合上报一些客户端浏览器的设备类型等数据,就可以实现简单的统计啦!
额,先看下兼容性如何:http://caniuse.com/#feat=nav-timing
这篇文章中 Demo 的运行环境为最新的 Chrome 的控制台,如果你用的是其他浏览器,自查兼容性哈~
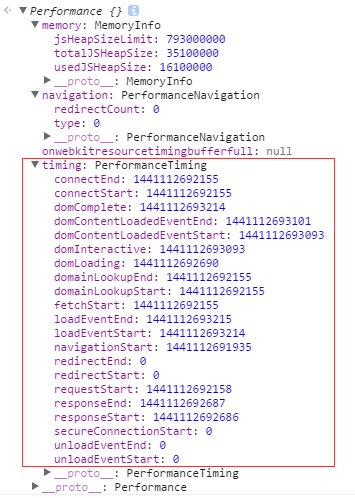
先来看看在 Chrome 浏览器控制台中执行 window.performance 会出现什么:
简单解释下 performance 中的属性:
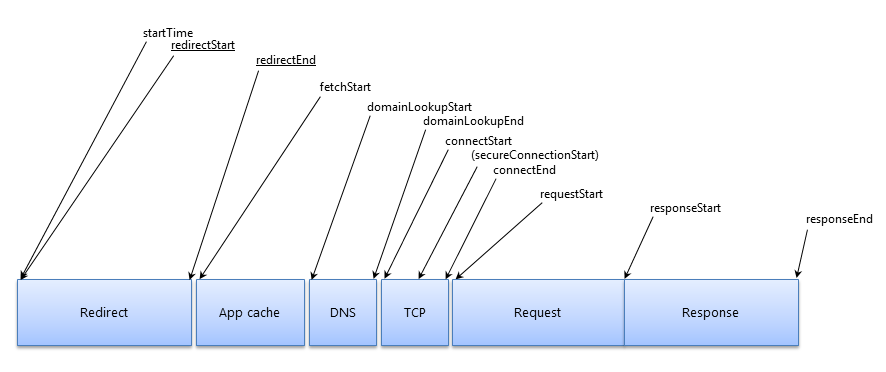
先看下一个请求发出的整个过程中,各种环节的时间顺序:
具体的含义都在注释里说明了,接下来我们看下能用这些数据做什么?
使用 performance.timing 信息简单计算出网页性能数据
在注释中,我用【重要】标注了我个人认为比较有用的数据,用【原因】标注了为啥要重点关注这个数据
使用 performance.getEntries() 获取所有资源请求的时间数据
这个函数返回的将是一个数组,包含了页面中所有的 HTTP 请求,这里拿第一个请求 window.performance.getEntries()[0] 举例。 注意 HTTP 请求有可能命中本地缓存,所以请求响应的间隔将非常短 可以看到,与 performance.timing 对比: 没有与 DOM 相关的属性:
-
navigationStart
-
unloadEventStart
-
unloadEventEnd
-
domLoading
-
domInteractive
-
domContentLoadedEventStart
-
domContentLoadedEventEnd
-
domComplete
-
loadEventStart
-
loadEventEnd
新增属性:
-
name
-
entryType
-
initiatorType
-
duration
与 window.performance.timing 中包含的属性就不再介绍了:
可以像 getPerformanceTiming 获取网页的时间一样,获取某个资源的时间:
使用 performance.now() 精确计算程序执行时间
performance.now() 与 Date.now() 不同的是,返回了以微秒(百万分之一秒)为单位的时间,更加精准。
并且与 Date.now() 会受系统程序执行阻塞的影响不同,performance.now() 的时间是以恒定速率递增的,不受系统时间的影响(系统时间可被人为或软件调整)。
注意 Date.now() 输出的是 UNIX 时间,即距离 1970 的时间,而 performance.now() 输出的是相对于 performance.timing.navigationStart(页面初始化) 的时间。
使用 Date.now() 的差值并非绝对精确,因为计算时间时受系统限制(可能阻塞)。但使用 performance.now() 的差值,并不影响我们计算程序执行的精确时间。
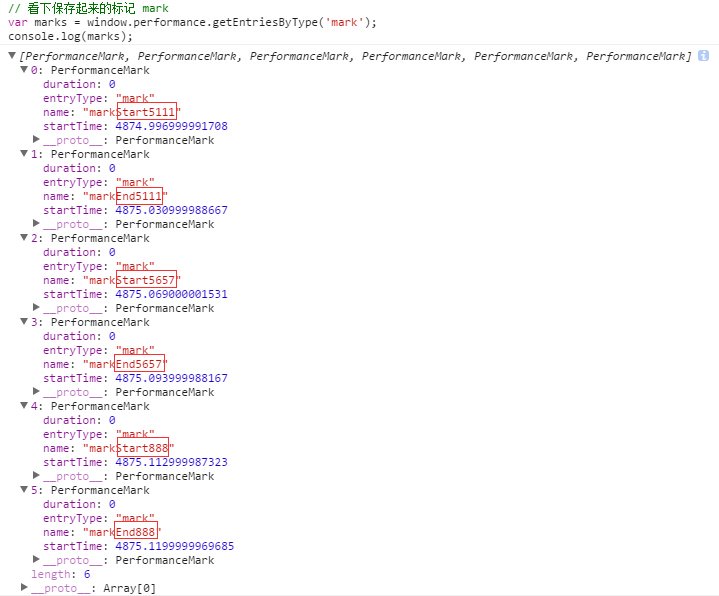
使用 performance.mark() 也可以精确计算程序执行时间
使用 performance.mark() 标记各种时间戳(就像在地图上打点),保存为各种测量值(测量地图上的点之间的距离),便可以批量地分析这些数据了。
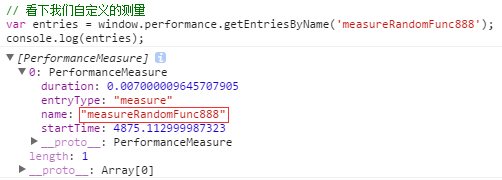
直接上示例代码看注释便明白:
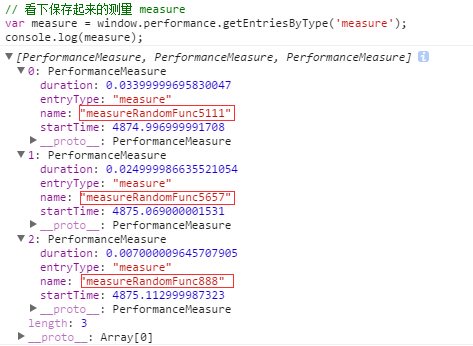
可以看到,for 循环 measureRandomFunc888 的时候
结束时间为: 4875.1199999969685
开始时间为:4875.112999987323
执行时间为:4875.1199999969685 - 4875.112999987323 = 0.00700000964
标记和测量用完了可以清除掉:
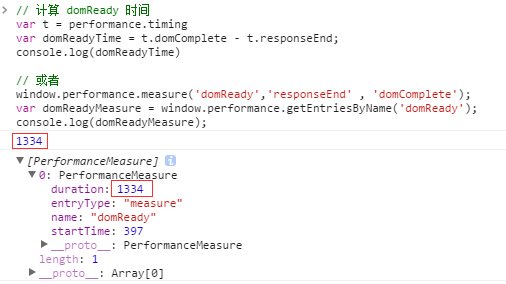
当然 performance.mark() 只是提供了一些简便的测量方式,比如之前我们测量 domReady 是这么测的:
其实就可以写成:
抛砖引玉:performance 数据能干啥用?
熟悉 Chrome 开发者工具的朋友应该知道:在开发环境下,其实我们自己打开 Chrome 的开发者工具,切换到网络面板,就能很详细的看到网页性能相关的数据。但当我们需要统计分析用户打开我们网页时的性能如何时,我们将 performance 原始信息或通过简单计算后的信息 (如上面写到的 getPerformanceTiming() 和 getEntryTiming()) 上传到服务器,配合其他信息(如 HTTP 请求头信息),就完美啦~




johe 2020 年 2 月 1 日
学习了 真的很不错的一篇文章
肥翔 2018 年 4 月 8 日
performance.now() 返回的是毫秒吧,只是小数点后面的值能精确到微秒
aleewr 2017 年 4 月 15 日
返回数据 domComplete 都为 0.
自由自在的我77 2016 年 12 月 25 日
// 计算程序执行的精确时间 function getFunctionTimeWithDate (func) { var timeStart = Data.now(); // 执行开始 func(); // 执行结束 var timeEnd = Data.now(); // 返回执行时间 return (timeEnd – timeStart);} 写错了吧,应该是 Date.now() 吧
vell0120 2016 年 10 月 17 日
问下怎么可以拿到资源大小呢?
橄榄123 2016 年 7 月 23 日
请教几个问题:1. 页面加载时间:performance.timing.loadEventEnd – performance.timing.navigationStart;2.Time-line 里面的 Range 时间 3.NetWork 里面的 Finish 时间三者有什么关系?
zyg 2016 年 1 月 7 日
深深吐槽一下 代码 阅读体验真心不好
冯瑞_FR 2015 年 11 月 4 日
[good]
joy 2015 年 10 月 15 日
hello。请问 window.performance.now() 返回的时间是当前时间的微秒值还是当前时间与 navigationStart 对应时间差值?
TAT小赖 2015 年 10 月 15 日
文中有写噢:『performance.now() 输出的是相对于 performance.timing.navigationStart(页面初始化) 的时间』
TAT小赖 2015 年 10 月 15 日
你在浏览器中 console 一下也便知。
TAT小赖 2015 年 10 月 8 日
鲁国人 2015 年 9 月 18 日
学习了!赞